Surgical robotics platform for tracking and imaging
Accomplishments: Published two papers to SPIE Medical Imaging Conference 2025 - San Diego, CA
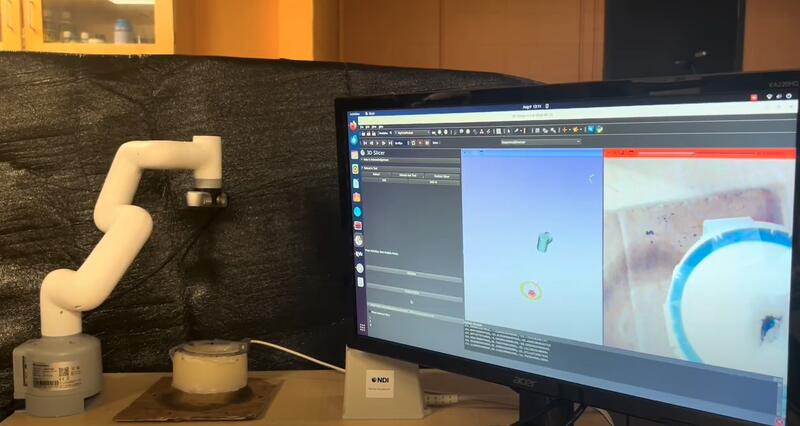
Part 1: Created a reusable, open-source module using ROS2 and 3D Slicer for scanning a phantom cavity using a depth camera scan, machine vision and spectroscopy. The 6-axis robot scans the entire cavity to detect cancerous tissue.
PURPOSE OF RESEARCH: Cancer can recur after tumor resection surgery if tumor tissue is missed and left behind. We hypothesize that intraoperative robotic imaging could be used to inspect the surgical cavity and localize residual cancer tissue. This technique has the potential to improve the success rate of tumor resection surgery. In this work, we propose and evaluate a benchtop testbed for robotic manipulation of an optical imaging probe and robotic optical tracking. We use low-cost hardware and open-source software to construct the testbed.

Part 2: Created a reusable, open-source module using ROS2 and 3D Slicer for optical tracking of a moving phantom. The 6-axis robot with a depth camera attached stays in a fixed orientation and distance relative to the moving phantom cavity.
PURPOSE OF RESEARCH: Roughly 40% of breast cancer patients are required to undergo corrective surgery after tumour resection via breast-conserving surgery (BCS). Sweeping of the cavity, resulting from the tumour resection, by spectroscopy and ultrasound imaging is emerging as a potential solution for identifying leftover cancer. However, the use of imaging modalities in the cavity is challenging as breast tissue is soft, malleable, and moves frequently. This paper presents and verifies an approach for tracking the relative motion of a resection cavity with a robotic arm.
Code available on GitHub.
